Littering has wreaked havoc on ecosystems all over the world. What do we do now to amend the global problem of chronic waste?
By Emily Folk
A single plastic bottle can take up to 450 years to degrade.
Today, we know the impact littering has on our environment and human health. With access to the Internet and social media platforms, we witness the havoc pollution has wreaked on ecosystems all over the world. Solving the littering issue can seem like an insurmountable challenge. However, there are ways to amend the global problem of chronic waste, even though it may initially seem overwhelming.
Kids learn the definition of a “litterbug” starting in elementary school and receive regular reminders not to throw trash on the sidewalk. For decades, the conversation around litter points the finger to the consumer—the person throwing trash out their car window or tossing food wrappers in the park.
When finding a solution to littering, we need to examine its history. Discussions for the past few decades have placed the responsibility of preventing litter on the individual. In actuality, much of the blame goes to the industries that create waste in the first place.
Litter isn’t the problem. It is simply a by-product of a convenience-oriented economy. If you look at the history of litter, there remains one constant. Production of trash, including plastic packaging and aluminum cans, has continued to grow. Despite efforts to reduce waste and promote recycling, corporations like Coca-Cola continue to produce plastic pollution at an unsustainable level.
Litter would not exist if it were not for the businesses that created disposable packaging and capitalized off their invention. The primary anti-litter campaign, Keep America Beautiful, was founded by the very companies producing the waste.
Sustainable solutions to litter involve looking at the role of the packaging and bottling industry. To truly put an end to littering, we need to put more accountability on corporations to reduce the amount of waste they create in the first place.
The Keep America Beautiful Campaign
Keep America Beautiful is perhaps the most well-known anti-litter movement in the United States. Founded in 1953, this organization works to inspire and educate people on improving their communities. Today, it leads initiatives such as the Great American Cleanup and America Recycles Day.
Volunteer efforts funded by this organization are significant in slowing environmental harm. Annual events take place all across the country. The collective effort results in an impactful reduction in waste pollution in public places and along roadways.
However, most people are unfamiliar with the organization’s origin. When states began responding to the litter problem, the packaging and beverage industry worried the message would undermine their business models. Their profits demanded disposable cans and food packaging. So they founded Keep America Beautiful, which put the litter problem back on the people and out of the hands of corporations.
The packaging industry relied on convincing people they needed to buy more stuff and that these items would undergo a cycle of becoming trash almost immediately. Society had to be trained to dispose of single-use plastic. The bottle and can industry used the power of advertising to convince consumers that the things they were reusing, like glass bottles, were garbage.
The Recycling Movement
Following the rise of disposable products, advertisers convinced Americans they needed convenience above all else. In the post-World War II era, marketers sold the American society the idea of microwaveable dinners they could consume in front of the TV. These companies also marketed plastic soda bottles that did not require reuse. In the 1970s, consumers became increasingly uncomfortable with the amount of waste sent to landfills.
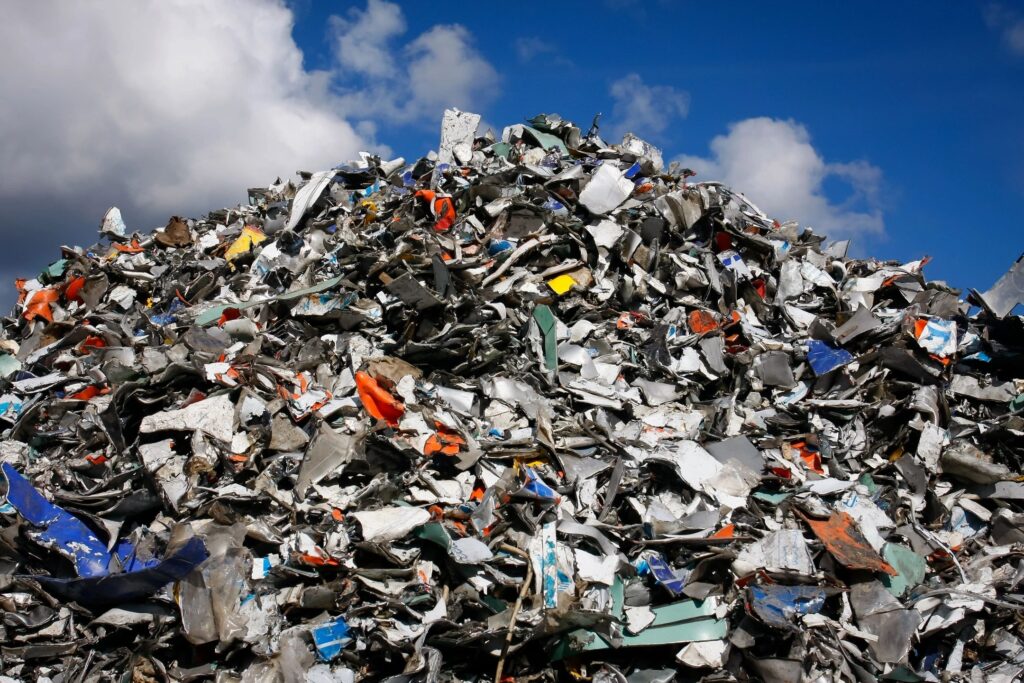


In response, Keep America Beautiful founded another organization, the National Center for Resource Recovery. With serious lobbying efforts, this initiative persuaded state legislators to favor recycling over reusing or reducing consumer goods. The Container Corporation of America invented and funded the phrase “reduce, reuse and recycle.”
By creating the recycling movement, corporations extended their influence across all levels of policy development. Most notably, they actively limited policies that would require corporations to take responsibility for their own waste management. Between 1989 and 1994, Keep America Beautiful spent over $14 million in lobbying efforts to limit recycling policies and let consumers bear responsibility.
The recycling movement has a dirty secret, too. For decades, anti-litter advertisements, including Keep America Beautiful’s infamous “Crying Indian” PSA video, have distracted consumers from making a real impact. Today, people are well-aware that recycling doesn’t always work. Corporations benefited from the recycling industry’s inefficiency, setting up recycling initiatives to fail from the beginning.
Most of the recycling collected by municipalities in the last thirty years has been shipped to China, where it was most often dumped into the ocean or added to landfills with little to no environmental standards.
Littering Corporations and the Circular Economy
The contemporary equivalent of the first anti-litter campaign is the corporate standard of a circular economy. Circular economies keep products and materials in continuous use, extending their lifetime and reducing the amount of waste generated from the system as a whole. Also referred to as a closed-loop system or cradle-to-cradle, the concept is only successful if it radically changes consumerism on a global scale — instead of making more plastic out of recycled materials.
If you look at the fashion industry, companies like H&M are making sustainability efforts that drastically overstate their ability to combat pollution. Creating clothes out of recycled materials may sound like a great idea, but if the growth potential remains the same, the impact does not change.
According to a study conducted by Greenpeace, Coca-Cola generates over 100 billion plastic bottles annually. A so-called circular economy may devolve into a form of greenwashing that enables unsustainable business models to persist without making real change. There is a real concern that the concept of a circular economy may award companies for their “sustainability” efforts while simultaneously allowing them to continue polluting at the same rate.
Recently, Coca-Cola has also announced a new initiative, launching their campaign of Coke bottles consisting of plastic from the sea. This concept might seem more optimistic if it were not for the fact that they are largely responsible for the plastic being in the sea in the first place. While the concept of a circular economy is promising, the way companies implement it will ultimately make the most significant impact.
Littering and the Individual
Modern consumers are demanding transparency. More so than ever before, buyers are supporting companies that engage in sustainable practices. People are increasingly aware that recycling is not a single solution. Lifestyles that advocate for buying less, like minimalism, are becoming mainstream. The solution to the worldwide littering problem is to hold corporations responsible for the waste they create. By advocating for smarter consumption, individuals can make a big difference in how materials become trash.
Buyers are widely knowledgeable of the impacts of waste pollution and are making efforts to ensure waste is handled more sustainably. City-wide green initiatives reduce litter and encourage recycling. Online companies promote the purchasing of secondhand products like clothes.
Individuals are managing their waste better while also holding the companies that create trash accountable. Organizations like Keep America Beautiful have helped in cleaning up the U.S.’s public places, sidewalks and roadways. Now it is time for them to take responsibility for the waste they generate before it reaches the consumer.
This article was originally published in the Conservation Folks blog on June 19, 2020.
Featured photograph provided by Boyce Duprey.


About the Author
Emily Folk is a sustainability and green tech writer. Her goal is to help people become more informed about the world around them and how they fit into it.